Creators have the right to control and protect their work from unauthorized use. However, understanding copyright law, especially renewal requirements, can sometimes be challenging.
Many creators wonder: How often do copyrights need to be renewed to keep their work protected?
The confusion often stems from outdated assumptions or misinformation about copyright terms, leading to unnecessary stress or unintentional loss of rights.
Below, you’ll learn how modern copyright terms work, the rules for renewal, and what actions, if any, you need to take to keep your rights intact. By the end, you’ll feel confident managing your copyright without second-guessing yourself.
- The Copyright Act of 1976 removed the renewal requirement for works created after January 1, 1978, granting automatic protection for the author’s life plus 70 years.
- Older works published before 1978 originally required renewal but were automatically extended under the 1976 Act and subsequent legislation.
- Works that entered the public domain due to missed renewals under pre-1978 laws remain permanently in the public domain.
Table of Contents
Do Copyrights Need to Be Renewed?
No, most copyrights do not need to be renewed today. However, whether renewal is required depends on when the copyright was created.
Copyright laws have evolved over time, and the rules differ significantly between older works, which were created before 1978, and modern copyrights, which were created after 1978.
Under the Copyright Act of 1909, works were initially protected for 28 years.
To maintain copyright protection, the owner had to file for a renewal to extend the term of copyright for an additional 28 years. If the renewal was not filed, the work entered the public domain.
For example, a book copyrighted in 1950 would have required renewal in 1978 to extend its protection. The Copyright Renewal Act of 1992 simplified this process for certain works, automatically renewing copyrights for works still under protection at the time.
However, the Copyright Act of 1976, which governs modern copyrights, removed the requirement for renewal.
For modern works created on or after January 1, 1978, copyright protection is granted automatically and lasts for the entire term specified by law, which is either the life of the author plus 70 years or 95 years for corporate and anonymous works.
If you’re wondering, how long does copyright last? The answer depends on the type of authorship and whether the work was created by an individual, jointly, or under a work-for-hire agreement.
How Often Do Copyrights Have to Be Renewed?
Copyrights do not need to be renewed under current U.S. copyright law.
Since the enactment of the Copyright Act of 1976, which became effective on January 1, 1978, copyright protection has been granted for the life of the author plus 70 years without the need for renewal. Below is a breakdown of how this works and what it means for older works.
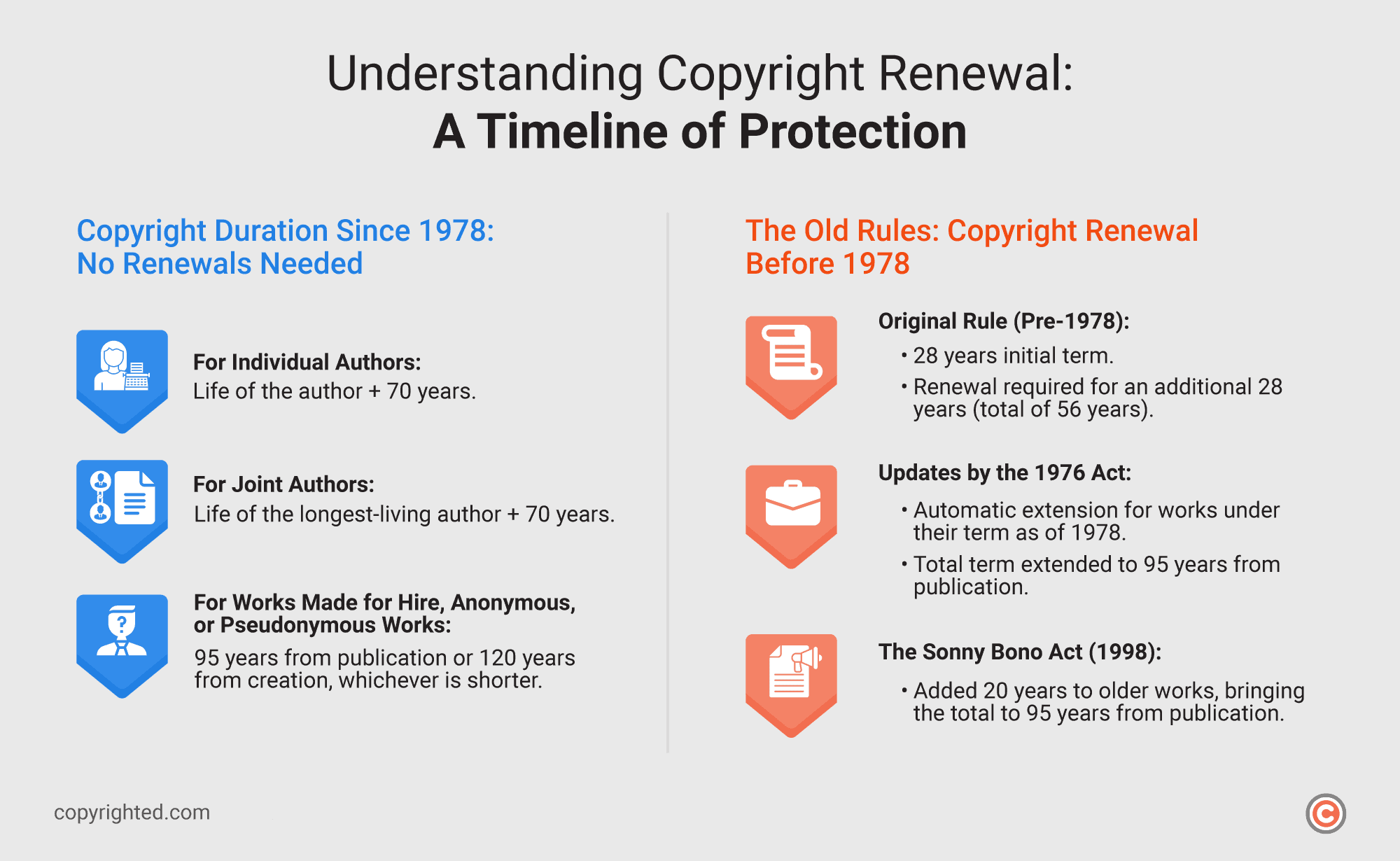
Copyright Duration for Works Created After 1978
For works created on or after January 1, 1978, copyright protection lasts for:
- Individual authors: The life of the author plus 70 years.
- Joint authors: The life of the longest-living author plus 70 years.
- Works made for hire or anonymous and pseudonymous works: 95 years from publication or 120 years from creation, whichever is shorter.
Under these rules, the duration is automatic, and no renewal process is required.
Renewal for Works Created Before 1978
For works published or registered before January 1, 1978, renewal used to be a necessary step. These works originally had a 28-year initial term and required a renewal for an additional 28 years, totaling 56 years of protection.
However, the Copyright Act of 1976 extended these protections without requiring further action:
- The 1976 Act granted an automatic extension for works still under their initial or renewal term as of 1978.
- The Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act of 1998 added another 20 years, making the total term for older works 95 years from publication.
Although modern copyrights do not require renewal, some authors or rights holders may still encounter references to renewal in older materials. If you’re working with a pre-1978 work, verifying its publication date and whether it falls under the old renewal requirements is important.
What Happens If a Copyright is Not Renewed?
For works created before January 1, 1978, failing to renew with the U.S. Copyright Office resulted in the work falling into the public domain.
Once a work entered the public domain, it lost all copyright protection, and anyone could freely use, reproduce, or adapt it without seeking permission or paying royalties to the original copyright holder.
Under the law at the time, the initial length of copyright is 28 years. Renewal was required during the 28th year to secure an additional 28 years of protection.
If the copyright holder did not file for renewal by the deadline, the copyright expired, and the work was no longer protected.
When a work fell into the public domain due to non-renewal, it became available for unrestricted use. This applied to all forms of creative works, including books, music, films, and visual art.
For instance, if a novel copyrighted in 1940 was not renewed by 1968, it became public domain material in 1968, allowing others to republish, adapt, or otherwise use it freely.
The transition of unrenewed works into the public domain was permanent.
Even though later laws, like the Copyright Renewal Act of 1992, eliminated the need for renewal, works that had already entered the public domain due to missed renewals remain there. They cannot regain copyright protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if a copyright expires?
Once copyright expires, the work enters the public domain and can be freely used by anyone.
Can you lose copyright protection if you don’t renew it?
Only works created before 1978 required renewal; failure to renew resulted in loss of protection. Modern copyrights do not require renewal.
Do you need to renew your copyright after 70 years?
No, modern copyrights last for the author’s life plus 70 years and do not require renewal.
How do you know if your work’s copyright needs renewal?
Check the publication date—only works published before 1978 might have needed renewal.
Are there any fees for copyright renewal?
Renewal fees are applied only to works under pre-1978 laws, which are no longer relevant to modern copyrights.


