Copyright laws were designed to protect creators, but the rapid growth of technology is making that harder than ever.
Digital content can be copied, shared, and distributed worldwide in seconds. Artificial intelligence is generating art, music, and literature, raising questions about ownership.
Global markets complicate enforcement, as laws differ across countries, and older works enter the public domain at different rates depending on jurisdiction.
These challenges lead to important questions about how copyright laws can protect creators while allowing innovation. They also raise concerns about the ownership of AI-generated content and whether the law can keep pace with the digital world, impacting artists, writers, businesses, and consumers alike.
This article explores the future of copyright, including ongoing legal debates and potential changes within the legal framework governing intellectual property.
- AI-generated content is reshaping copyright law, raising questions about authorship, fair use, and the role of human creativity.
- New technologies are improving copyright management by enabling better content tracking, automated royalties, and more efficient enforcement.
- Future copyright laws will likely focus on balancing creator rights, innovation, and stronger enforcement against digital piracy.
Table of Contents
How Has Copyright Evolved Over Time?
Copyright has been around for centuries, evolving alongside creativity and technology. While its main purpose remains the same, which is the protection of works created by artists, writers, and musicians, laws have changed to address new ways of producing and sharing content.
From book publishing to digital media, lawmakers have introduced new protections to handle emerging challenges. Here are key milestones in copyright law:
- Statute of Anne (1710): The Statute of Anne is the first official copyright law in Britain, granting authors exclusive rights for a set period.
- U.S. Copyright Act (1790): Influenced by the Statute of Anne, the Copyright Act of 1790 is the first U.S. copyright law protecting books, maps, and charts.
- Berne Convention (1886): The Berne Convention is an international agreement ensuring automatic copyright protection across member nations.
- Copyright Act of 1976 (U.S.): Expanded copyright to cover new media. The Copyright Act of 1976 also introduced the “fair use” concept.
- Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) (1998, U.S.): The DMCA focused on digital content protection and anti-piracy measures.
- EU Copyright Directive (2019): The EU Copyright Directive updated copyright laws for the digital age, defining responsibilities for content-sharing platforms.
As technology advanced, copyright laws expanded to cover various creative works. What began with books later included photography, film, music, and digital content.
Here’s a look at how copyright adapted to major innovations:
- Printing Press (15th Century): Early copyright laws regulated book reproduction.
- Photography & Film (19th-20th Century): Legal protections extended to visual media.
- Broadcasting & Music (20th Century): Copyright covered radio, television, and recorded music.
- Internet & Digital Media (21st Century): Laws like the DMCA addressed digital copying and piracy.
- Artificial Intelligence (Present): Legal debates now focus on AI-generated content and digital ownership.
Each change reflects an effort to protect creative rights while allowing public access. As technology continues to evolve, copyright law will keep adapting.
Technological Advancements Impacting Copyright
New technologies are changing how content is created, shared, and protected. As innovation advances, copyright laws must adapt to the digital world.
Below are some of the most significant technologies shaping the future of copyright.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI can generate art, music, literature, and even software, raising important legal questions:
- Who owns AI-generated content? Under most copyright laws, only human-created works qualify for copyright. The U.S. Copyright Office has ruled that purely AI-generated content cannot be copyrighted.
- What about AI-assisted works? Some jurisdictions recognize copyright in AI-assisted creations if a human provides meaningful creative input.
The debate over copyright in the age of artificial intelligence will likely influence future legal decisions, determining how AI-generated content is protected and monetized.
Blockchain and Digital Ownership
Blockchain technology secures digital assets through non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and smart contracts. This impacts copyright by:
- Verifying ownership: Digital artists use blockchain to prove and track ownership of their work.
- Automating royalties: Smart contracts allow creators to receive payments automatically when their work is resold.
- Enforcement challenges: Blockchain records ownership but does not prevent copyright violations or unauthorized duplication.
Some regions, such as the European Union under the Digital Services Act, are exploring how blockchain can support copyright enforcement.
Streaming and Digital Content Platforms
Streaming services like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube dominate content distribution, leading to changes in copyright enforcement and revenue models. Key legal aspects include:
- Licensing and royalties: Platforms must obtain rights and compensate creators, often through collective licensing.
- Content takedowns: The DMCA requires platforms to remove infringing content upon request.
- AI copyright enforcement: Tools like YouTube’s Content ID automatically detect copyrighted content but sometimes flag legitimate material by mistake.
As streaming continues to grow, lawmakers are debating fair compensation for creators and platform responsibilities.
What is the Future of Copyright Law?
Copyright law is on the verge of major changes as new technologies challenge existing rules. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and digital platforms have raised complex legal questions about ownership, fair use, and enforcement.
Lawmakers will need to adjust copyright policies to protect creative rights while allowing innovation.
AI-Generated Content and Copyright Protection
AI-created content is one of the biggest areas for potential reform. Under current laws, only human-made works qualify for copyright. This leaves uncertainty about AI-assisted creations.
Some countries may introduce legal definitions to recognize human contributions in AI-generated works. Others may require companies to obtain licenses for copyrighted material used in AI training.
Changes to Licensing and Fair Use
Licensing rules may also evolve as digital content moves across borders. There is an increasing demand for a global licensing system, as a standardized approach could simplify royalty payments and ensure fair compensation for creators.
Fair use laws under 17 U.S.C. § 107 may also see revisions. AI-generated content and transformative media, such as remixes and reaction videos on platforms like YouTube and TikTok, have raised questions about the limits of legal reuse.
Clearer guidelines could help define fair use in the digital age.
Stronger Copyright Enforcement
With digital piracy becoming more advanced, copyright holders are pushing for stronger protections. AI-powered copyright detection tools are improving, but they sometimes flag legal content by mistake.
Lawmakers may need to regulate automated enforcement systems to prevent wrongful takedowns while ensuring creators’ rights are upheld.
How to Stay Compliant With Future Copyright Changes
Creators and businesses must stay informed to protect their intellectual property and avoid legal risks as copyright laws evolve. Keeping up with legal changes, using the right tools, and following best practices can help ensure compliance.
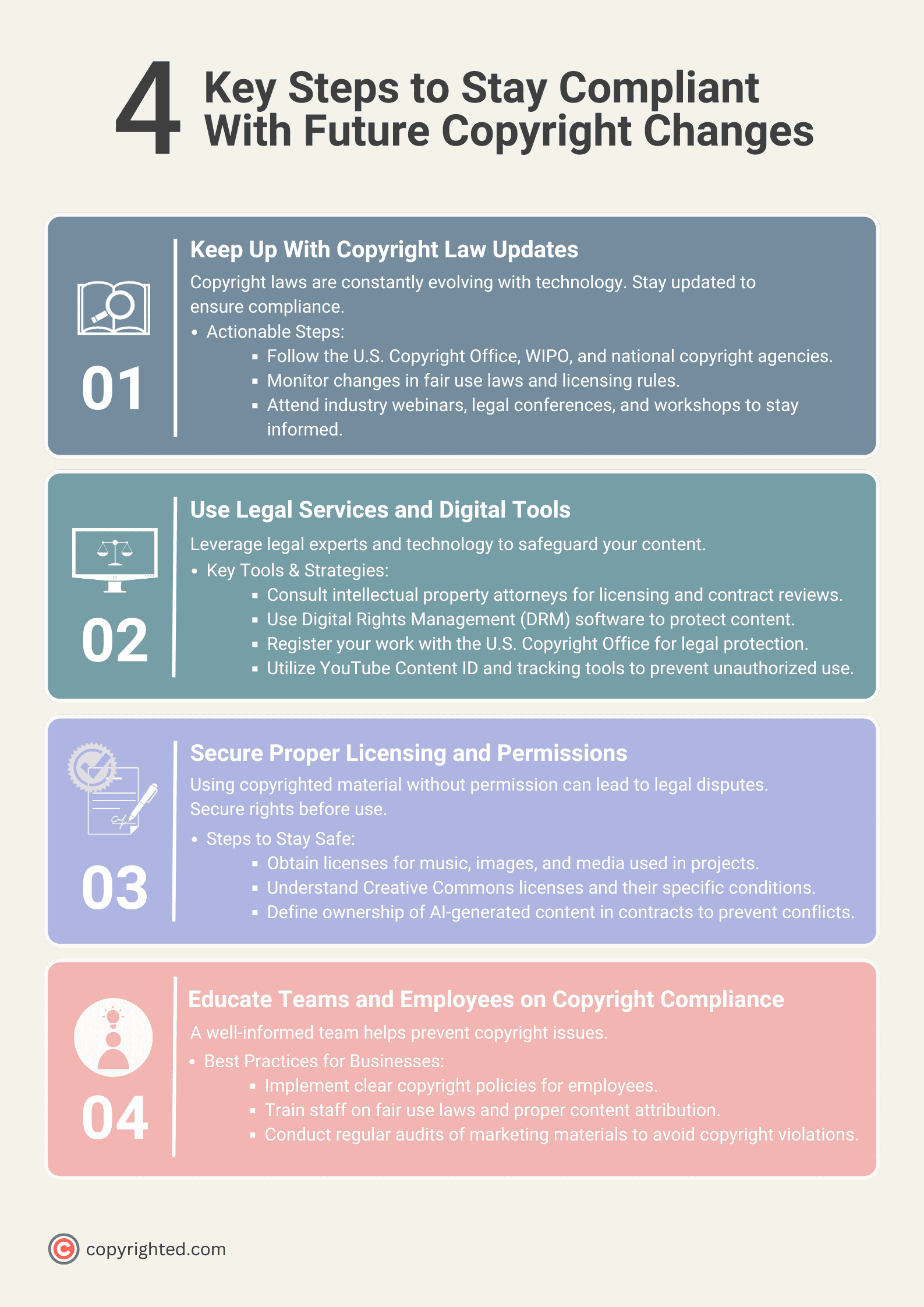
Keep Up With Copyright Law Updates
Copyright laws change over time, especially as digital media, AI, and blockchain technologies influence legal decisions. Staying informed is essential for creators and businesses that rely on copyrighted material.
Here’s what creators can do:
- Follow updates from official sources like the U.S. Copyright Office, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), and national copyright agencies.
- Monitor legislative changes, such as updates to fair use provisions and new licensing frameworks.
- Attend industry webinars, legal conferences, or workshops focused on intellectual property rights.
Use Legal Services and Digital Tools
Copyright law can be complicated, but legal services and digital tools help simplify the process. Working with an intellectual property attorney can provide valuable guidance on licensing agreements, contract reviews, and copyright filings.
To prevent unauthorized use, many businesses rely on digital rights management (DRM) software to safeguard their content.
Copyright registration with the U.S. Copyright Office under 17 U.S.C. § 408 establishes official recognition and strengthens legal protection in potential disputes of copyright infringement.
Platforms like YouTube also offer content ID systems, allowing creators to track and manage their copyrighted material more effectively.
Secure Proper Licensing and Permissions
Using copyrighted material without permission can lead to legal issues. To avoid infringement:
- Obtain proper licenses for music, images, and other media used in business or creative projects.
- Understand Creative Commons licenses, which allow limited use of copyrighted works under specific conditions.
- For AI-generated or co-created works, clarify ownership rights in contracts to avoid disputes.
Educate Teams and Employees on Copyright Compliance
Businesses should treat copyright compliance as a shared responsibility. Setting clear policies on intellectual property use helps prevent unintentional violations while educating employees on fair use laws, licensing requirements, and proper content attribution reduces legal risks.
Regular audits of content and marketing materials ensure continued compliance and help catch potential copyright issues before they escalate into legal disputes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main challenges facing copyright today?
The rise of AI-generated content, digital piracy, and differences in global copyright laws make enforcement and ownership more complex.
How can technology help combat digital piracy?
AI-driven content detection, blockchain-based ownership verification, and automated takedown systems help protect copyrighted materials.
How can creators benefit from new copyright technologies?
Blockchain ensures verifiable ownership, smart contracts automate royalty payments, and AI tools help track and manage content usage.
Will creators have more control over their digital works in the future?
Emerging technologies like blockchain and AI-powered enforcement likely improve copyright management and licensing options.
Will globalization affect copyright protection?
Yes, global markets complicate enforcement, but international agreements like the Berne Convention aim to standardize copyright protection.


